SHORT
In the relatively short time since enterprises began adopting generative AI, they have already started adapting their approach to leveraging this technology. They are now confronting several challenges that have emerged, including the high costs associated with large-scale use of large language models (LLMs), inadequacies in their cloud and data infrastructure, concerns about the reliability of generative AI outputs, and the complex risks related to regulation, intellectual property, and ethics. Rather than relying on a single vendor, enterprises are increasingly using multiple model providers to develop their generative AI applications. Additionally, they are turning to more cost-effective open-source models that they can control and refine, rather than investing in the costly and complex process of building custom models from scratch. This approach aligns with what McKinsey research refers to as adopting the role of a generative AI model “taker” or “shaper” rather than a “maker.”
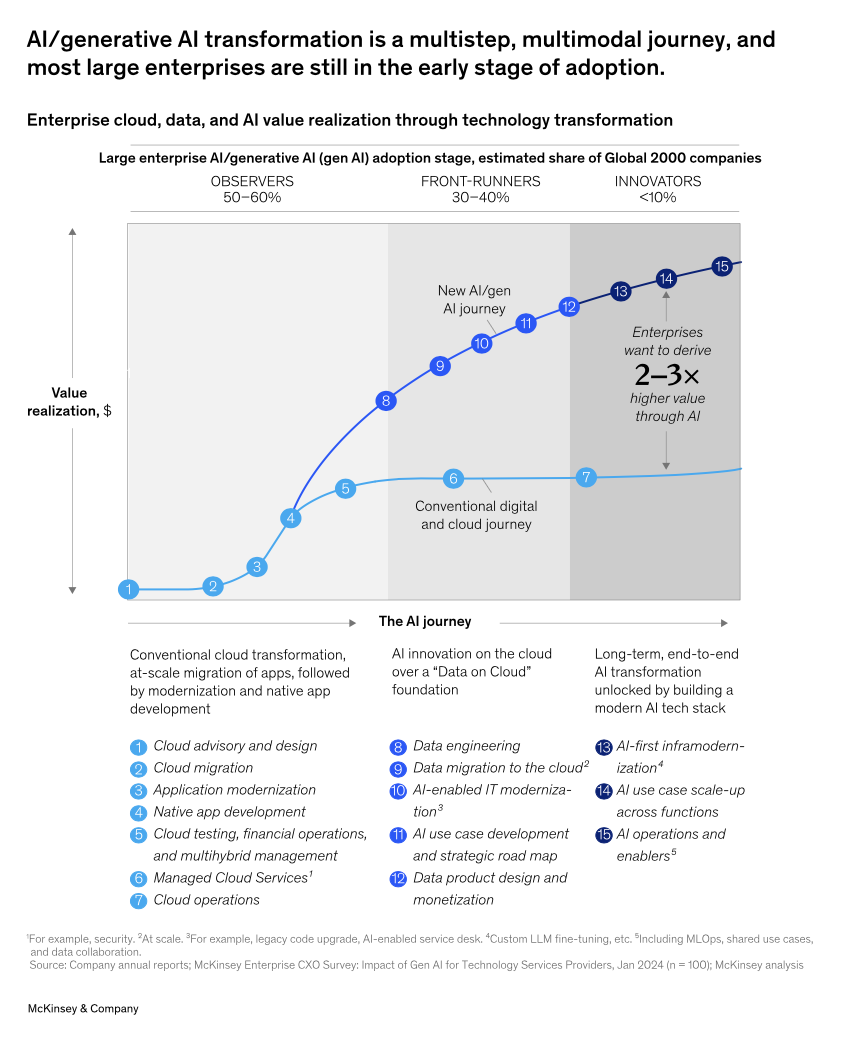
Despite these widespread changes, enterprises are at varying stages of generative AI adoption. Our analysis categorizes organizations into three stages of readiness and adoption:
Observers: The majority (50-60%) are “observers,” focusing on AI readiness by establishing their data and cloud foundations and conducting small-scale proofs of concept (POCs) for internal use cases, such as text summarization and knowledge management, aimed at enhancing productivity.
Front-runners: Another 30-40% are “front-runners” with a clear vision for using AI and generative AI to scale cost reductions through applications like AI-enabled service desks and legacy-code upgrades. These organizations have restructured their operations by creating AI centers of excellence (COEs) and new roles such as chief AI officer.
Innovators: Less than 10% are “innovators” who are AI-first and have integrated strategies to achieve cost reductions and unlock the full potential of generative AI. They focus on advanced use cases like AI-enabled product design and development to drive future business growth.
In brief enterprises are adapting to generative AI by using multiple model providers and cost-effective open-source models to overcome high costs, infrastructure challenges, and regulatory risks. They are at varying stages of adoption, with the majority focusing on AI readiness, some scaling cost-reduction efforts, and a few integrating advanced AI strategies for future growth.
@McKinsey #GenAI #AI









Karel Doomm2
AI Integration principles, by BCG:
✔ Start with a Clear Business Use Case – Identify problems where AI adds tangible value, rather than deploying AI for the sake of innovation.
✔ Establish Governance & Compliance Frameworks – Set up internal policies to mitigate AI risks and ensure accountability.
✔ Invest in Talent & Training – Equip employees with AI literacy and domain-specific expertise to maximize adoption.
✔ Leverage Hybrid AI Models – Use a mix of cloud-based and on-premise AI solutions for better control and cost efficiency.
✔ Monitor & Iterate – Regularly evaluate AI performance and refine models based on real-world feedback.
TomK
Key Challenges in Enterprise AI Adoption
– Data Privacy & Security – Ensuring compliance with regulations (GDPR, CCPA) and protecting sensitive business data from AI training models.
– Model Reliability & Bias – Generative AI models can produce inaccurate or biased outputs, impacting trust and usability.
– Cost & Infrastructure – Running large AI models requires significant computational resources, making cost optimization a priority.
– Integration with Existing Systems – Seamlessly embedding AI into current workflows without disrupting productivity.
– Regulatory & Ethical Considerations – Navigating evolving AI regulations and ensuring responsible AI use.
TomK
Generative AI is transforming industries, offering new opportunities in automation, content creation, and decision-making. However, for enterprises, the adoption of GenAI is not just about integrating new technology—it’s about aligning AI capabilities with business goals while managing risks and scalability.
Karel Doomm2
Great insights on the evolving landscape of generative AI in enterprises! The breakdown of adoption stages—observers, front-runners, and innovators—really highlights how organizations navigate challenges like cost, infrastructure, and regulation at different maturity levels. As AI continues to reshape business operations, balancing scalability with responsible implementation will be key. Looking forward to seeing how companies refine their strategies in the coming years!