The machine learning technology proves that today’s computers are acquiring ever more astonishing skills. Perhaps their ability to take in and process newly acquired knowledge will one day enable them to sustain artificial intelligence. What exactly is the computer’s ability to learn?
We are naturally delighted to see babies smile when they recognize our faces as we lean over them. We are amazed to see little ones utter their first words as they repeat after us. Then comes the time when a child begins to make up stories about the fairy tale characters we have read to it about. Finally, it learns to count, draw, write and correct its first school paper. And then one day we hear it express opinions about the world. Opinions that are often so extraordinary they leave us in shock. At this moment, we are witnessing a human being becoming intellectually independent.
Machines that smarten up
It is not only people that learn from experience by acquiring knowledge from the outside world. We are now witnessing a time when sophisticated information technologies are also emerging from infancy. One development associated with Artificial Intelligence that captures the imagination of the entire world is machine learning. The name itself hints at a field of fully automated processes that rely on intelligent data processing and smart decision-making. AI is where the most ambitious R&D work is conducted in today’s world.
Machine learning, or limited self-sufficiency
Machine learning is a field positioned on the borderline between mathematics, statistics and programming, i.e. information technology. Its goal is to create complex algorithms capable of reaching optimal decisions and, even more importantly, continuous self-improvement. The algorithms that underpin machine learning are specific and highly sophisticated. By and large, they rely on a dynamic model that processes inputs (data) to make specific decisions. What is significant is that such algorithms have the ability to “self-learn” as they actively process the datasets that are entered. However, the entire mechanism has one serious limitation. And that is, as the computer executes its tasks, it draws on experience of the “supervisor”. What it means is that man – a programmer, operator or teacher – critically influences the way information is processed. His or her job is to support the machine by entering data batches, manually checking the conditions that result from analyses and remove system blockages. The computer’s self-sufficiency therefore continues to be limited as it depends on an expert. The general consensus is that the first people to witness machine learning were the IBM experts who tried to develop algorithm to help chess players improve their game. A landmark along the path came with the development of the Dendral IT system at Standford University in 1965 which automated chemical analyses. It is now recognized that the research led to the first computer-discovered compounds.
Some the latest research seeks to eliminate or at least strongly reduce the teaching role played by humans to ensure that algorithms learn independently.
Time for unlimited self-sufficiency
One of the most intensely explored areas today in the field of machine learning is deep learning, viewed as a subcategory of the former. Extensive mathematical structures that support multi-strand processing, referred to as neural algorithms, are capable of making decisions, correcting them by learning from their mistakes and, based on prescribed models, selecting from the available sets the data that most accurately addresses a given question or problem. In other words, they can learn independently using the deep learning method. Deep learning supports e.g. voice recognition, natural language, translation from various languages and image recognition. All these functions are particularly interesting to corporations such as Facebook and Google.
Deep learning systems are designed to emulate the workings of the human brain with its powerful neural networks. Such networks are what allows computers to learn independently without human supervision. In essence, such systems comprise large numbers of parallel processors fed massive amounts of data, including specifications for complex relationships between data. The networks use unlimited flexibility as neurons can be combined into layers. Every layer provides the next one with the results of the previous one until a task is solved.
By and large, a computer’s ability to learn, i.e. improve its operation, results from a single cause. Neural networks are collections of interconnected nodes. Each time a computer acquires a new experience or takes action, its connections reorganize themselves. They become ever more perfect allowing the machine to perform its assigned tasks more efficiently. The fact that computers adapt independently through the experience they gather rather than through a programmer’s interference was a breakthrough in the development of IT and its commercial applications. The main driver of interest in neural networks is unabated demand for structuring and searching through information. In the Big Data era, deep learning technology is our great ally.
Watson will tell you the whole truth
This may sound odd giving one an impression we are discussing equipment hidden away in military laboratories. But that is hardly the case. Deep learning is moving out to the streets and into our homes. The IBM-made computer, known more appropriately as artificial intelligence IBM Watson, can analyze huge sets of data. This incredibly efficient machine shows the possibilities brought to users with the advent of machine learning and deep learning mechanisms. Computers understand the questions asked in a natural language. As they search for answers to such questions, they go through a variety of vast datasets having to do with business, mathematics, medicine and law. IBM Watson relies on the ability to increase its capacities with each successive task. The more data the machine absorbs and the more tasks it receives, the greater its analytical and cognitive abilities.
The proliferation of such machines is precisely what today’s business and medicine are counting on. For that reason, any self-respecting technology corporations is making every effort to employ the solutions adopted for this ultra-efficient computer as broadly as possible. Similar solutions are being developed by Elon Musk as well as Google, Facebook and Microsoft.
How to win in the Chinese game of “Go”?
A curiosity as well as a good illustration of the above mechanisms and differences between machine learning and deep learning is the famous story of a computer defeating masters in the Chinese game of “Go”. Its rules allow for an almost infinite number of combinations of stones on the game board. (Compared to “Go”, chess is a simple game). First and foremost, the Google-developed algorithm Alpha Go enabled a computer to analyze millions of games played by humans (a case of supervised learning from a limited dataset). Much greater impact on the computer’s success came from the machine’s ability to analyze another set of situations unfolding on the game board – these resulted from the machine playing against itself (deep learning)! Needless to say, such work was only possible with the use of powerful servers and the cloud technology. It is nothing other than the availability of processing power that paved the way towards the incredible success of the Google algorithm.
We are all benefitting
The impact of intelligent machines is bound to be particularly profound in a range of areas. Tesla’s autonomous vehicles would be inconceivable without the technologies I am describing. One of the reasons why self-driving vehicles can navigate roads is their ability to read and analyze the images they encounter. Machine learning also has implications for the way information is structured. Consultancies that conduct their studies with the use of hundreds of millions of data points gain powerful analytical tools. Another likely beneficiary is the medical world Any instrument that allows medicine to model the behavior of the human body is worth its weight in gold. In another article, I described a contemporary client who demanded that the global market respond with a fully individualized services that are available on a moment’s notice. Learning machines are just the means to make that possible. Large Internet-based retailers such as Amazon use state-of-the-art algorithms to present their offerings on clients’ monitors in ways that are both better and faster.
Humanity’s collective knowledge at one’s fingertips
As mentioned earlier, the commercial implications of the technologies in question are increasingly more visible for the average user. Thinking machines that rely on them will provide man with access to growing amounts of knowledge of the kind that has previously been unavailable and could not be processed. The greatest breakthroughs that may result from the spread of such technologies are likely to occur in medicine and financial markets. I think it will take two or three years at the most for major changes to be seen clearly. Such changes are bound to impact all of us personally in a huge way.
Related articles:
– What a machine will think when it looks us in the eye?
– Blockchain – the ultimate financial crash
– Synthetic biology. Matrix, Dolly the Sheep and the bacteria of the future
– The lasting marriage of technology and human nature
– Blockchain has a potential to upend the key pillars of our society
– The brain – the device that becomes obsolete
– Artificial Intelligence – real threats or groundless fears?
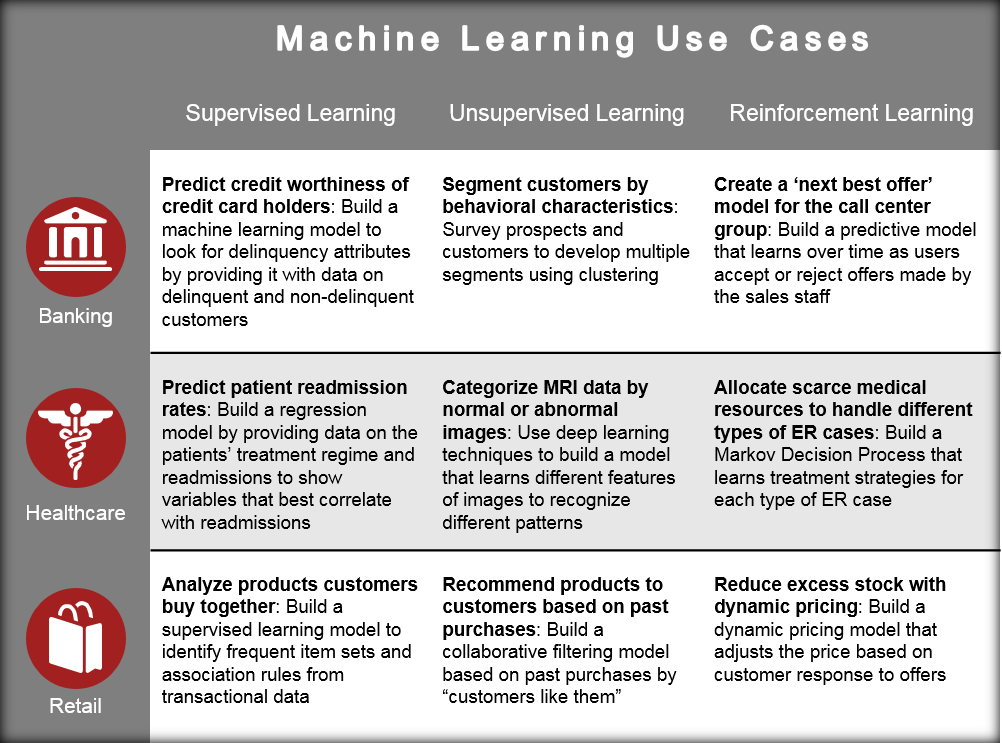
Machine Learning Use Cases. Link

Machine Learning Infographics. Developed by Todd Jaquith and The Futurism Team








Adam T
Good read. Thank you
Karel Doomm2
Very thoughtful and informative article for a lay person such as myself to understand AI concepts.
Simon GEE
Why did Google open-source their core machine learning algorithms? It’s simple. Machine learning algorithms aren’t the secret sauce. The data is the secret sauce. Data = money. Huge money
John McLean
Many issues involving erroneous and imprecise data arise in data collection for machine learning per se, as much data is simply wrong. New and advanced algorithms are needed to be designed that can distinguish real data from artificial and poor data, thereby improving the reliability of the data gathered. Artificial data and data with poor signal quality play a major role in this analytical difference. Many times, analysts are overwhelmed by the complexity of data collected, but ML algorithms that can identify and streamline the most pertinent data without leaving behind other crucial information need to be developed. Moreover, ML algorithms that can allow the AI to explain the reasoning behind current data understanding is necessary.
DDonovan
Perhaps there is an argument that treating a machine that resembles an animal poorly has ramifications to people to people or people to animal interactions. However, there is no need to protect a robot besides the policies already in place for protecting machines and property.
Adam Spikey
Hi Norbert, How much space do I have to respond? We should be extremely concerned and I am going to write short concerns and then several links and two by Paul Michelman from Editor In Chief, MIT SLoan Management Review. Paul is on the network and you may want to reach out to him. Concerns: No Global Governance, No International Laws, Tech Companies trying to influence policy makers, Policy makers may be unclear or unfamiliar with complexity of problem to write policy, AI Mind Labs harvesting data off of sites from people that are unfamiliar they are being studied, Technologists changing human biology and we are giving coders a key to humanity, Cyborg technology is now live with the interface with the brain, Cyber attacks brought upon society like a Perfect Storm with AI technology, Under reporting of cyber attacks due to lack of controls and ransom is paid by companies. There is more… Have a great weekend.
DDonovan
Deep learning can detect more granular or more sophisticated data or analysis. I believe we should use it as part of our AI devotes tools since it enables a higher degree of trust and automation. Deep learning is not so far away from machine learning. It’s only more precise 🙂
JohnE3
But it’s not only about AI. ML could be used for a more simpler tasks line voice recognition, translation, command and control, self-dev. Coud be very usefull for so to speak self-reprogramming
TomHarber
Not only. I would rather say ML fits perfectly if you want to crack more complex issues based on big data modeling, statistics. Way beyond human recognition. Next level is deep learning – which is more way advanced than ML
TomCat
See this. Facebook has now taken the initiative to monitor its network actively for hints that someone may be contemplating to commit suicide. It has created an Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithm that looks for typical patterns in social media posts that may mark out a potential suicide. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/03/facebook-is-using-machine-learning-to-prevent-suicide/
Norbert Biedrzycki
Interesting. But it’s not clear they’re using ML. It’s rather simple prediction based on a user patterns, as stated in the article. But still interesting to read
TommyG
I do not agree. This time is full ML. Please see process flow descriptions available on their pages
Don Fisher
This new ML neuro networks training can either be attributed with a new tag of data flow, or the creation can carry multiple tags. While the first scenario is more practical, this solution may leave businesses with the problem that individual parts cannot be traced back to their origin. A solution may be that the one tag attached to the object makes reference to the different sources of all individual parts. But, if composed objects keep all the tags of integrated parts, tracing all relevant information concerning that object becomes extremely complex and difficult. Sounds complex but check link provided for an explanation
Mac McFisher
ML is quite straight-forwad in terms of logic behind. It focuses on developing algorithms and software based off of the sysytem’s past experiences. A program capable of machine learning is able to perform a certain task or improve how it performs a task through previous multiple runs and without any additional changes in the software. In the fewest terms, machine learning is the extraction of knowledge from data and past runs of data computation. No more nor less
Adam Spark Two
Humans are merely extremely complex machines. Machines in their current state cannot feel emotions, but as technology progresses, machines will have the capacity to learn, to feel emotions, and eventually may surpass even our brains. Emotions are essentially series of electrical pulses sent throughout the brain, which can be replicated by a machine. Though at a very basic level.
Karel Doomm2
For example, ML can be used to predict mortality and length of life remaining using physiological patient vitals and other tools including blood test results, either in the immediate future, such as for a traumatic car accident, or in the long-run, such as for cancer. Most significantly, ML models can be used to help physicians diagnose patients, especially in cases involving relatively rare diseases or when outcomes are hard to predict. Moreover, machine learning can be used to determine the most effective medication dosage, reducing healthcare costs for the patients and providers.
John Accural
If I understood the concept correctly, it doesn’t require someone to monitor each input and tediously train a machine.
Instead the system looks through thousands of items, picks up on recurring patterns, then groups common patterns into ad-hoc categories.
A person then looks at what is significant about each category and tells the system like in picture recognition: “that category is cats”, “that category is people”, “that category is dogs”. Then once each category has been labelled, the process can then look at new pictures and say “that fits very well in my ad-hoc category #XX, which has been labeled ‘cats'”.
johnbuzz3
You can have the best of all worlds in the future of you want. Having synthetic body and high density DNA brain housed within that synthetic body, and your mind is constantly synced to the cloud in the event of unforseen accident. Future is so bright.
TomK
We all know machine superintelligence it is coming sooner or later, but the question in the minds of almost everyone is: should humanity fear that? Everyone knows that when machines become smarter than human beings, they tend to take over the world. Correct? Many of the world’s smartest minds — like Stephen Hawking, Elon Musk, and even Bill Gates — warn about this kind of future, that in fact machines could be a threat to humanity
johnbuzz3
R. Kurzewil predicts that superintelligence as a singularity will not happen before 2030
TonyHor
.. and right now he’s changing his view saying that in 2029 it will happen for sure. See leatest interview
Jack666
What does it mean superintelligence?
Norbert Biedrzycki
WIKI 1: A superintelligence is a hypothetical beeing that possesses intelligence far surpassing that of the brightest and most gifted human minds. A superintelligence may or may not be created by an intelligence explosion and associated with a technological singularity.
WIKI 2: Or an intellect that is much smarter than the best human brains in practically every field, including scientific creativity, general wisdom and social skills.
Adam Spark Two
Once upon a time on Tralfamadore there were creatures who weren’t anything like machines. They weren’t dependable. They weren’t efficient. They weren’t predictable. They weren’t durable. And these poor creatures were obsessed by the idea that everything that existed had to have a purpose, and that some purposes were higher than others.
These creatures spent most of their time trying to find out what their purpose was. And every time they found out what seemed to be a purpose of themselves, the purpose seemed so low that the creatures were filled with disgust and shame.
And, rather than serve such a low purpose, the creatures would make a machine to serve it. This left the creatures free to serve higher purposes. But whenever they found a higher purpose, the purpose still wasn’t high enough.
So machines were made to serve higher purposes, too. And the machines did everything so expertly that they were finally given the job of finding out what the higher purpose of the creatures could be.
The machines reported in all honesty that the creatures couldn’t really be said to have any purpose at all. The creatures thereupon began slaying each other, because they hated purposeless things above all else. And they discovered that they weren’t even very good at slaying.
So they turned that job over to the machines, too. And the machines finished up the job in less time than it takes to say, “Tralfamadore.”
Kurt Vonnegut – “The Sirens of Titan”
CaffD
Very good. Classic from my old times. I remember reading this years ago. Thank you for brinnging back great memories
TonyHor
Thank you. Good reminder of a old times 🙂
Adam Spark Two
Let’s think for a while about potential job market for ML specialists or even so called Data scientists. There are some companies that require their data scientists to code low level for performance reasons. Example of industries: content creation, retail, video/audio streaming, ad sales, lead gen, analytics products, etc. Or in other words, most of the tech sector focused on consumers and everyday businesses (non-finance, non-scientific), chances are you won’t be digging deeply into the code with regularity. Most of these jobs at places like mentioned above is in understanding business problems and then building a bunch of intuition and knowledge about your data and domain. In other words charting and statistics. Also, some data engineering, or ETL type work. So, a potential job offering is huge. There are jobs which are beeing created by introduction of AI, Machine Learning, Automation
John McLean
Really interesting talk, mainly about detecting bad performance when dealing with unlabeled distribution
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZD8LA3n6YvI
TomHarber
Machines are laerning by themselves. But what about human evolution over time? If thinking was all that was needed, human technology would have advanced to where it is now thousands of years ago. Humans weren’t any less “intelligent” years ago. We haven’t changed or evolved biologically as a species in this time. We’ve just grown in numbers, come into more and more frequent contact with each other’s ideas, and devised more and more effective ways to share information. That’s all. Machines are overcoming us already in terms of spped, logic, mathematical straightforwardness. It’s not us getting “smarter.” it’s machines beeing faster