As we know, the Internet changed the world profoundly and, considering how fast it happened, dramatically. Now, there is another big breakthrough coming fast around the corner: blockchain. I explained how blockchain technology works in an article I posted last year. Now, I would like to discuss its potential to become a universal tool offering useful applications to just about every industry and sector.
Blockchain is a universal transaction register that can record and track any operation made in it. It is distributed throughout the Internet in thousands of unmodifiable copies via a peer-to-peer model, secured with sophisticated cryptographic protocols.
It can best be compared to an accounting ledger – a publicly accessible, global book of accounts that allows users to register and view financial transactions, property deeds and contracts. The information on who has executed a given transaction is confidential, disclosed solely to its owner. The open nature of blockchain will thoroughly revamp the financial sector, with some supervisory and transactional parts of the sector becoming obsolete. Transactions and information exchanges will become more transparent, faster and significantly less expensive, significantly reducing the cost of operating the financial system throughout the world. Institutions such as banks, stock exchanges and financial brokerages already can see the incredible potential of the technology, and they also understand the threat it poses to the status quo.
One ledger to rule them all
One of the key features of blockchain technology is that every user of this “ledger” acquires access to a copy of it, and that a change made to one copy is automatically registered in all others. It is a distributed system, which means there’s no central site for data processing.
Security, which is of paramount importance in such an open system, results from the application of mathematical algorithms and cryptographic rules. Blockchain can record sale and exchange transactions, authorizations, electronic signatures and practically any operation that validates any sort of asset.
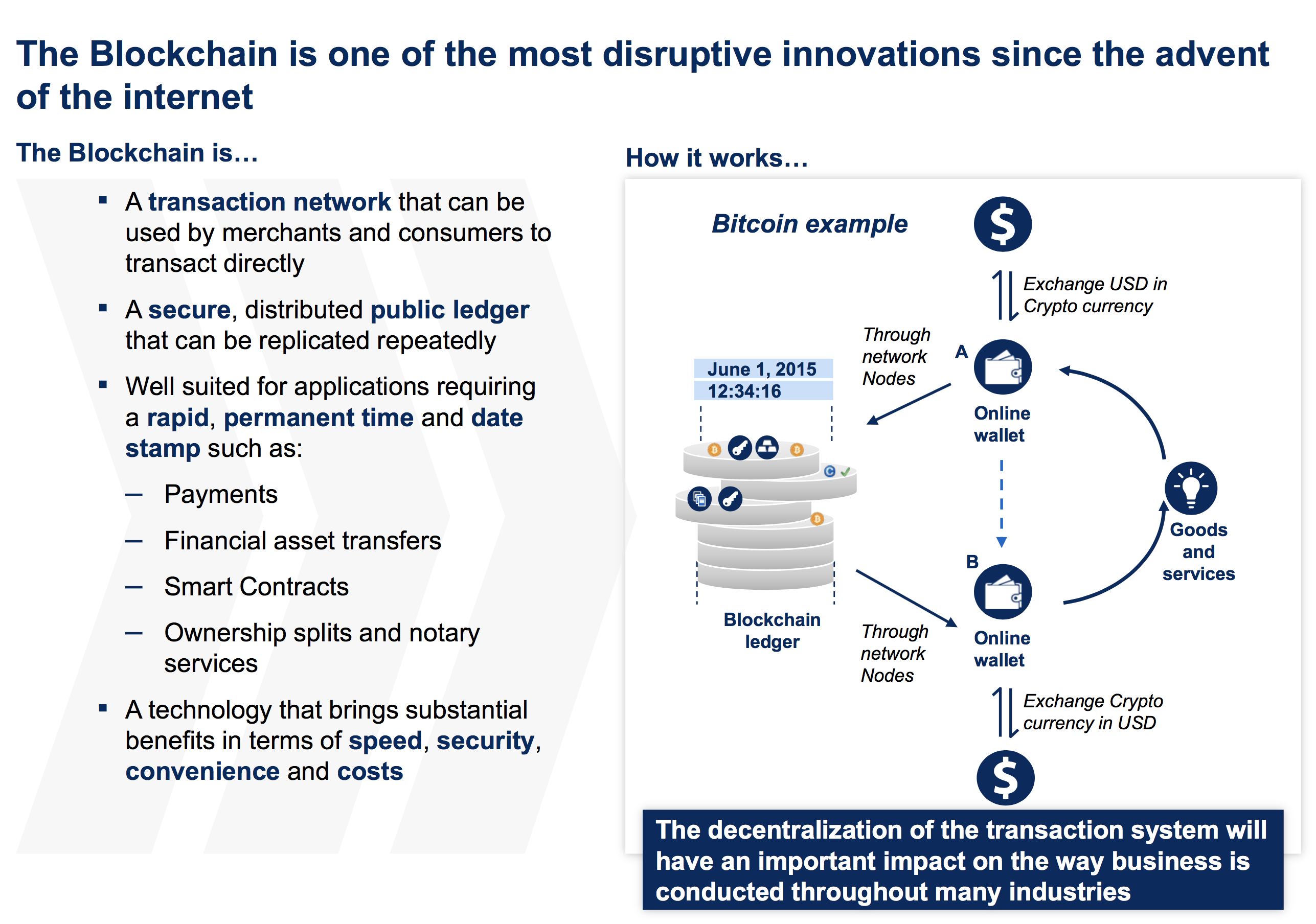
How blockchain works. Source: McKinsey
It is still about money
Experts believe that blockchain will need to be improved for another dozen or more years to become a truly global system. Today, blockchain is viewed primarily in the context of the cryptocurrency market – especially the bitcoin (BTC) – the first currency alternative to the official financial system. One could see the world of cryptocurrencies as a laboratory in which the strengths and weaknesses of the technology are tested through continuous use.
The idea of a cryptocurrency as a tool independent of the central financial system aligns with technology’s (and the internet’s) foundational ethos: openness, accessibility, and anti-hierarchical. Blockchain is designed to have no profit-earning intermediaries (there are still some today, but this piece of the puzzle is expected to evolve). Ultimately, the cost of using this system may be negligible, certainly compared to the benefits this can bring to individual and business users.
Blockchain will continue to grow. But many questions arise with respect to its spread, one of them its scalability, which is potentially unlimited.
For now, the financial sector has been the fastest to take notice of blockchain’s potential benefits. However, this is only the start. Things today are comparable to the stage of development that the Internet reached in the mid- 1990s. No one then could imagine the revolutionary impact of Internet 2.0. These are still early days, but perhaps a tipping point – Blockchain 2.0 – will arrive as soon as 2019. At that time, financial institutions will unroll many blockchain-based tools. By 2025, blockchain should become as integrated into our lives as the internet is today.
Earlier this year, the McKinsey Global Institute published a report that pointed to nearly 70 businesses that have already adopted blockchain technology. Nearly all of them are either financial or insurance companies. It is the insurance industry, says the report, that will benefit the most from the breakthroughs that the new technology promises.
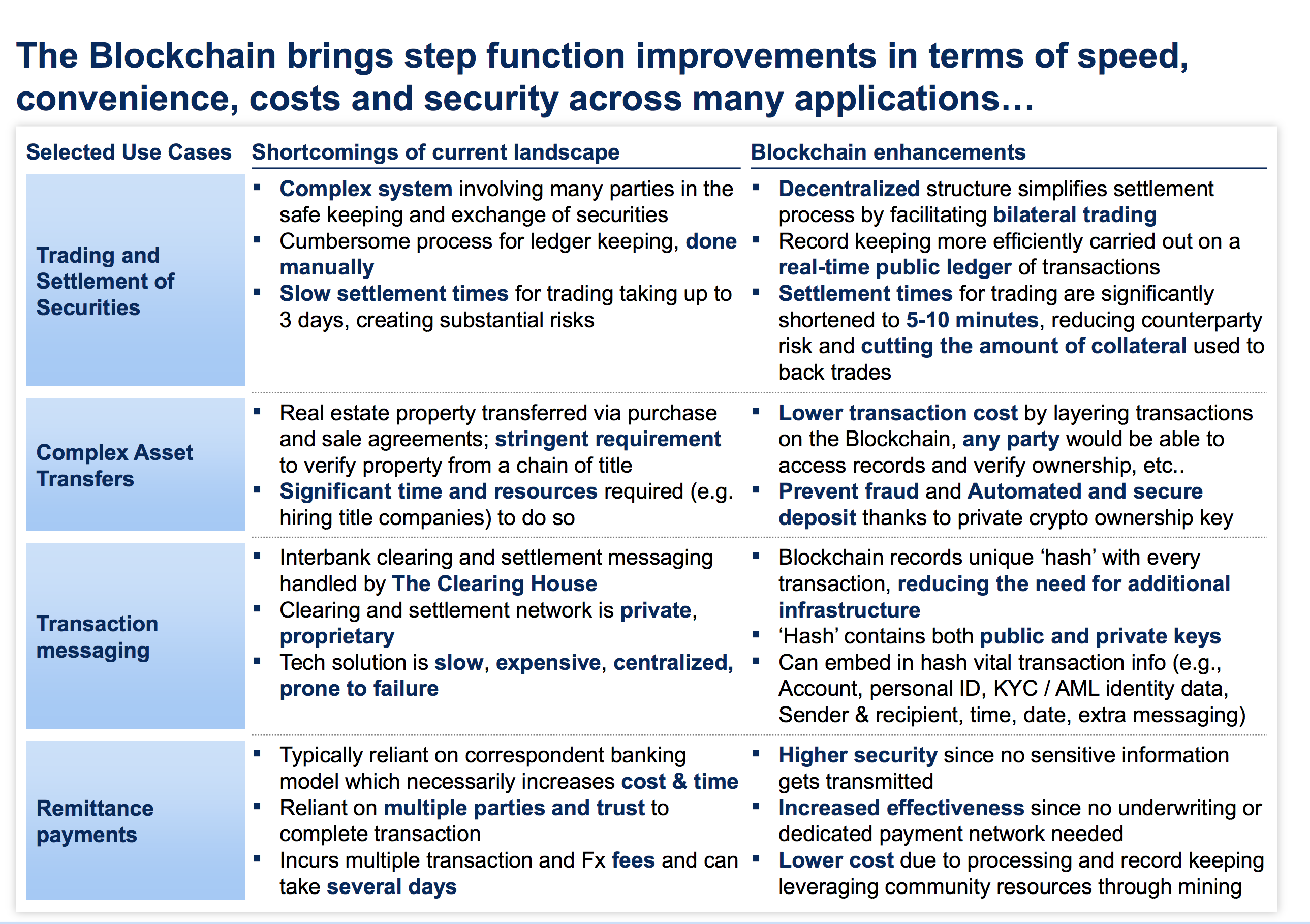

Example of blochchain applications in financial industry. Source: McKinsey
The blockchain future
At this point I would like to point to these realms in which blockchain should become operational the soonest and work best because of its structural characteristics.
1. Blockchain has REVOLUTIONIZED information flows
Data organization models vary in terms of the speed at which search results or other information is provided to users. In many cases, a qualitative change in the functioning of any organization, or in its competitiveness, depends on the way in which it organizes critical data. If access to such information can be improved, the entire organization’s operating model can be transformed, making the company work more efficiently. Note that decentralization and information sharing in blockchain encourages data exchange. This benefits all levels of management in any organization promoting its development.
2. Blockchain is TRANSPARENT
Transparency enables technology use wherever desirable, if not absolutely required. Hence, the organizations most interested in blockchain may be governmental entities that collect data on the functioning of public authorities and institutions. Wherever the citizenry has a right to access public information, blockchain offers a way to deliver on that promise.
3. Blockchain has an unlimited CAPACITY to process large data sets
Cloud technology currently allows the handling of trillions of bits of unintegrated data. Blockchain can combine and integrate such data in a logical way. In the Internet of Things, in which various devices rely on continuous information processing, blockchain will work perfectly. For airports, which process information on the weather, air traffic, security, time and passenger control, blockchain will be a natural ally. Similarly, smart buildings, or even entire smart cities, where sensors, software and algorithms are used to manage energy, water consumption, temperature, home appliances, television, alarms and cameras, generate huge amounts of data when connected to the internet. All these devices work together, and blockchain can improve the reliability of these interactions. Indeed, a simple application based on distributed technology may at some point be used to control every device or device set, ranging from home electronics to large fleets of autonomous vehicles.
4. Blockchain cuts out MIDDLE MEN
In a sense, blockchain is a more perfect embodiment of peer-to-peer technology. It allows users to exchange files directly, thereby revolutionizing the way we will use music or video files, greatly eliminating the involvement of all the middlemen who profit by distributing content. For example, people enabled to pay for a service directly, and to exchange data strings with service providers, need not worry about extra distribution fees. Blockchain can therefore empower consumers and provide them with instant and unlimited access to services at significantly lower price points.
5. Blockchain keeps data SECURE
Access to sensitive data, such as health information, must be fully controlled. Blockchain prevents most data leakage. While it is still possible for access codes to be broken and character systems stolen (and such violations do happen), it takes enormous computing power and huge amounts of money to commit such crimes. Therefore, blockchain technology will frustrate all but the most highly-resourced hackers and criminals and offers benefits to every institution that must guarantee confidentiality to clients and/or citizens, such as hospitals and insurance companies.
6. Blockchain enables convenient information EXCHANGE
Blockchain’s encryption protocols make traditional ways of exchanging content, such as email and the cloud, less attractive. The system also makes it possible to publish and keep any content completely up to date, automatically. Thus, it may change the way research institutes – which depend upon updating data continuously – function. In fact, any institution that handles invoices, documents, electronic keys, access codes or any authorization tools should be interested in blockchain technology, even if they don’t yet know it.
7. Blockchain has the potential to ERADICATE poverty and ease access to financial markets
There are still a great number of areas around the world whose residents have no access to banking. With blockchain, a person who, for physical or financial reasons, is unable to use banking services, gains a new tool and, with it, becomes an empowered consumer. Armed with a smartphone, and cryptocurrency to pay for any services, unbanked consumers can even the playing field. Plus, an institution that wishes to allocate funds for development – for instance, to a farmer, far from a bank branch, in a remote corner of the world – can do so directly and securely, no mediation required.
Is this a utopia?
The list above is only the beginning. I could point out many other industries, sectors, and social organization where blockchain would work equally well. Admittedly, spinning out the possibilities of this distributed, secure, universally accessible and trustworthy database that is quickly becoming the world’s primary and essential ledger sounds a bit utopian. (I also admit that blockchain’s highly mathematical and algorithmic nature gives me the awesome sensation of touching the essence of technology). But I have no doubt that blockchain will bring with it internet-level improvements to all our lives, and I cannot see a downside to that.
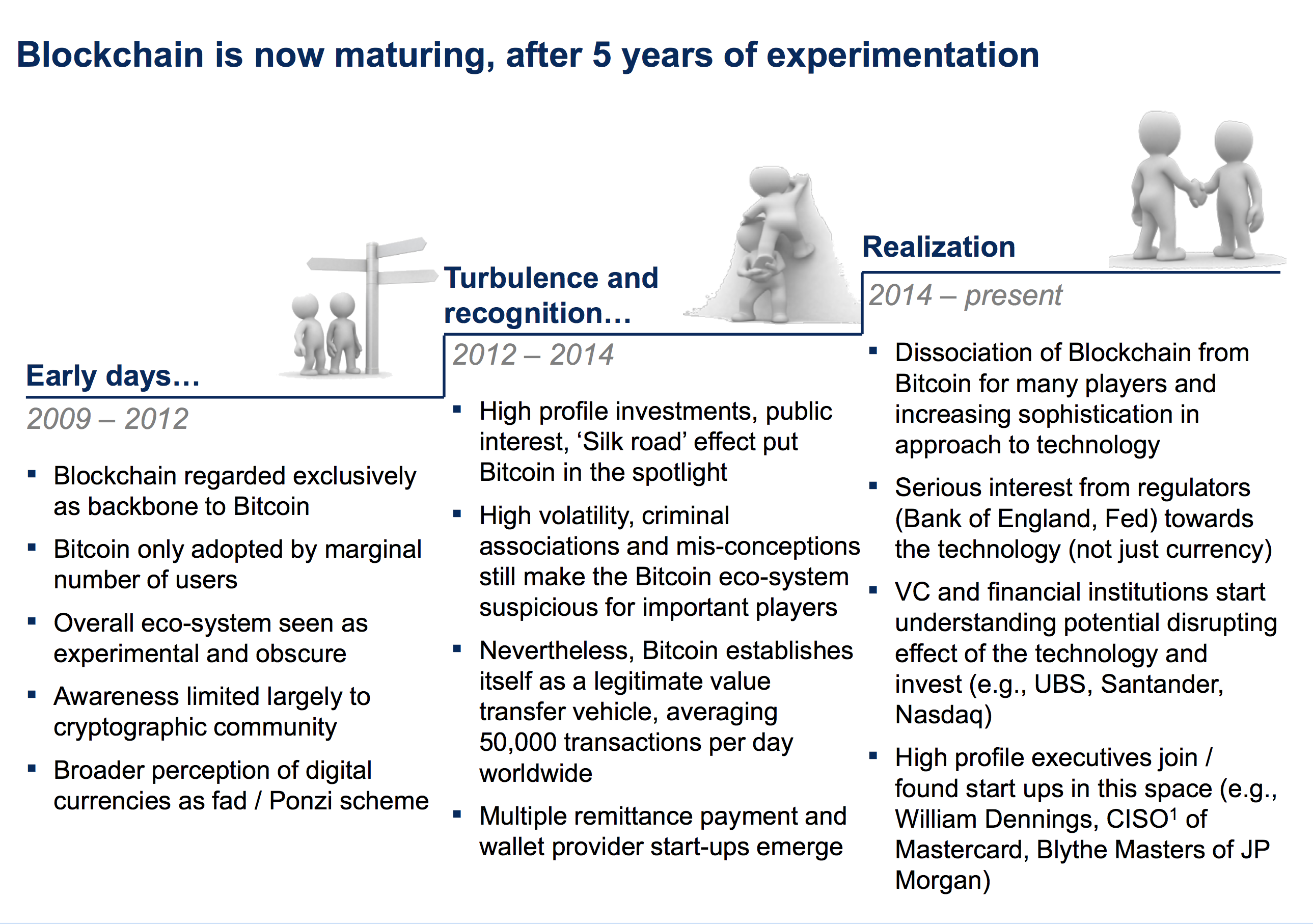
Blockchain is now maturing. Source: McKinsey
Related articles:
– Why do we care about blockchain technology?
– Blockchain – the ultimate financial crash
– Blockchain – the Holy Grail of the financial system?
– What is blockchain? All you need to know
– What are the bitcoins? All you need to know
– Blockchain has a potential to upend the key pillars of our society









Adam
Great read
Simon GEE
Well done
ZoraBora
The fundamental problem in working in the space of individual actors is that of the alignment of incentives.
The best developed systems so far are the ones that rely on the incentivised behavior of other individual actors to enforce their validity (courts enforcing your contractual expectations).
Blockchain creates new tools to constrain perverse incentives, though it also creates some perverse incentives of its own.
The success of blockchain (or any incentive constraining technology such as laws or social structures) will be dependant on its value for managing perverse incentives. This is roughly the difference of the perverse incentives it eliminates less the perverse incentives it introduces.
Current systems achieve value through very deep layering to create accountabiity (which tends to fail towards the top, as .01percenters tend to distort the social fabric that they touch and create perverse incentives of their own) .
Blochain tech potentiates strong incentive management without the extensive infrastructure depth, with each instance including a self contained (if brutally simple and inflexible) judiciary and enforcement component, free of internal perverse incentives. This offers huge potential efficiency gains…. But these are tools we are just beginning to understand how to integrate into our existing incentive management systems.
JohnE3
This is a P2P technology. One way to see what kind of benefits it has is to compare it to similar technologies and extrapolate.
Remember Napster? It was the first attempt at music piracy. This was like the banks: centralized with single points of failure.
After everybody at Napster got busted and people started freaking out, then torrenting became popular. uTorrent and other clients made it possible to share files P2P. This is like blockchain technologies: P2P based system, decentralized…not totally anonymous but okay on VPN/TOR…
Blockchain benefits over regular payment processors is almost the same benefits torrenting has against warez/centralized Napster-style file sharing platform.
Smart contracts, though, are a whole other beast
TommyG
Let’s say I want to build the next Kickstarter. I have to set up a webserver, database server, and something to take credit card payments, make sure I comply with everybody’s terms of service, start a business and pay accountants and lawyers to make sure I won’t get in trouble with all this money I’m handling, etc. Then I have to set fees high enough, do a bunch of marketing, watch my cash flow, make sure the servers keep running, and probably hire people to help.
Or I can write a couple pages of code and post it to a blockchain that supports smart contracts. From then on I don’t have to touch it. I can market it however much I like, but it’s not as stressful because I have no outgoing cashflow. I don’t even have to charge fees. I can forget the whole thing and people can keep using it as long as they like.
Zidan78
See another one -> India’s Aadhaar System: India is in many ways the perfect landing ground for blockchain ID solutions, thanks in part to Aadhaar, one of today’s digital wonders of the world. Aadhaar is India’s national ID system and the largest biometric database in history. It has about 1.2 billion members, each of whom gets a 12-digit ID number that is tied to biometric information. It’s considered proof of residency in India and is tied to the ability to access a range of government services.
https://www.finder.com.au/indian-municipalities-are-kicking-off-their-own-blockchain-id-tests
Tom Jonezz
India undertook a massive project called the India Stack, which is the establishment of a new digital biometric ID system. This system includes the fingerprints & iris scans for each of its citizens along with a 12 digit number consisting of the digital ID — since 2010 over 1.2 billion people in India have been issued with such IDs. This process is the largest IT project roll out in the history of the world. This has also enabled for the immediate authentication of the individuals.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Real blockchain use cases @101Blockchains
ZoraBora
Yes, hence why smart contracts are not actually a solution to every problem. The people who are proclaiming this are con artists. Virtually all the examples this article mentions (Ripple etc), I think ultimately are scams.
That doesn’t mean blockchain has no use. There exist problems that can be effectively contained entirely within it.
TomCat
It’s ~50%, and after one use, it’s 128 bit security, which is equivalent to Bitcoin’s security. It’s statistically possible for it to be higher or lower. https://iota.stackexchange.com/questions/245/what-information-is-leaked-if-i-reuse-an-address
I guess you are insinuating that this is a bad tradeoff for quantum security? If so, I’d like to point out that wallets can be automated to deal with the issue and permanent address solutions are being created, so it’s a temporary inconvenience for a long term security measure. My guess is other coins will have to find solutions once quantum computers come online, and unless they have a plan in place and tested, they won’t have much time in which to work–as we are seeing with BLT it may have effects on other parts of coin design, so kicking the can down the road in hopes that quantum computers are a distant problem may not be the wiser option.
TomK
IMHO the lack of trust is caused by lack of knowledge.
Adam Spikey
Blockchain provides accountability, transparency, and traceability for the value chain of a company and its supply chain processes and more. Some of the commodities industry understand the value gained by having accountability for their business units by use of blockchain technologies. Eventually, more successes with these blockchain platforms will be commonplace for all commodities, not just precious metals. Blockchain technology can move on to most industries and sectors from lumber to automotive.
Tom Jonezz
TradeLens — a blockchain based shipping solution that IBM & the shipping giant Maersk had been working on for almost a year came out of beta recently. The collaborative effort between the two companies has already garnered the support of 94 participants & 20 ports and terminals around the globe with 154 million shipping transactions already recorded on its blockchain. The project involves three components: Blockchain for tracking goods from start to finish, APIs to build applications on top of the platform & data standards for all the entities involved. Supply chain management has just gotten a blockchain upgrade. Similar projects are being implemented at the micro level as well.
TommyG
Anything can be owned (Money, Stocks, Asteroids and Ideas). Currently, things we own and transfer ownership of involve middlemen who extract value. Blockchains are the new middlemen who extract virtually no value.
JohnE3
Blockchains as a technology have the potential to automate all these industry interactions that are currently done by third parties. Blockchains could do for supply chains, clearing houses, escrow deals, and any other third party service what computers have done for every business and occupation they have touched.
Karel Doomm2
Gonna put voting on the blockchain? Great. How much energy are you going to waste to secure this block chain? Cause corporations or wealthy individuals would never use their wealth to affect the outcome of an election. Last presidential elections spent something like $7 billion. If someone could just get a bunch of servers and do a 51% attack for like $500 million dollars, it would be a good investment. Also, keep in mind, other nation states never interfere with elections….
So you need to probably burn a billion dollars worth of energy just to secure the election. Something like that. Maybe more if China wants to pick the next U.S. president.
Tom Jonezz
The blockchain-based digital tokens are seen as a direct threat to the traditional Fiat currencies which are believed to be replaced by them at some point in future once the scalability, volatility & regulatory issues are sorted out – it’s only a matter of when not if. We are so used to owning physical assets with “tangible value” that buying a cryptocurrency or any other digital asset for that matter scares most of us.
ZoraBora
The data in current auto history services is full of errors, typos, and incorrect data. With blockchain you don’t have the ability to correct your records, and leaves you open for extortion. Now a shady mechanic can shake you down for cash, otherwise they will enter an accident on your vehicle history.
Blockchain won’t solve the issue of you have to trust the data that is being inserted. It solves the issue of I don’t trust Carfax or Experian, to accurately report the vehicle history that it was given. In my experience that isn’t an issue we have.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Five common blockchain myths: limitations and advantages. It’s not only about cryptocurrencies
Oscar2
#1 bitcoin is also software framework (for public blockchain network implementations)
#3 temper-proof depends on blockchain software used / consensus algorithms & theory of fault tolerant distributed systems
TommyG
Bob opens a candy shop called “Bob’s Handy Dandy Candy shop” .
He has no idea how taxes and all this adult stuff work so he asks his older brother Charlie (a smart IT guy) to write him a magical SmartContract that cares about everything. He just needs a buyer to show the QR code Charlie gave him.
Alice comes by to buy some chocolate. She scans the QR code with her way to expensive phone and sends the amount to the SmartContract Charlie made.
This contract automatically orders new chocolate and pays for it. The chocolate is already on its way to “Bob’s Handy Dandy Candy shop”. The taxes are calculated and stored in the SmartContract. This cares about paying the taxes and tells the taxman some other stuff in order to make him happy. The rest gets transferred to Bob’s account. This all happens magically and faster as Bob can say “Thank you”.
After the first day he buys a ticket for the film “Frozen” from the money he just earned. He only has to copy the address code which the cinema has on their website. He sends the amount of money and the name of the film to this address. The magical SmartContract of the cinema sends the ticket back.
Bob coincidentally meets Alice in the cinema. Both loved the film.
TomHarber
Transparent – ok. But security is an issue
TommyG
Fantastic read! Thank you for sharing.
AndrewJo
This is only possible by removing the 20 year old security technologies that current Blockchain was built on and layer on Identity with privacy protective mechanisms
CaffD
Another interesting read. Like your posts a lot 🙂
TomCat
Without proper Identity it will be possible for bad actors to continue to create the same chaos thats occurring today. You will need to be securely authenticated with the system and have the proper access controls to the information. Massive privacy issues related to publicizing transaction information over a public network/ledger. As a result of this problem the majority of the capital market industry is focused on development of private/permissioned DLT that will never allow an Internet based browser access to these private networks. Access will likely occur via proprietary applications or proprietarty+embedded Webkit technology. By linking credentials to individuals, individuals and assets to corporate entities we can create unique cryptographic identification tagging to tradable instruments. Wrapped within a permissioned based privacy friendly security layer it will allow association of people and assets within a hostile environment (such as a public Blockchain running on the internet). This will allow authorized parties to utilize mathematical forensics to trace the chains of ownership yet prevent regulatory snooping. Some will argue that this is a only on-ledger work effort but even ledger work requires on-ramp, off-ramp, data updates, and linked data to off ledger sources.
TomHarber
The integrity of public blockchains for crypto-currency has made it a “futuristic integrity wand” to be waved at every problem. Except blockchain doesn’t even solve most problems of trust. The integrity of data on a public blockchain can be trusted not to change, but that says nothing about whether the data is right in the first place. […] Not for nothing do so many blockchain start-up pitches focus on the technology, as if it were inherently better to bring blockchain to x , rather than leading with the solution to a real-world problem. They are tokens in search of users as an end in itself.
Tom Jonezz
but don’t get me wrong, it’s really interesting piece
Tom Jonezz
List of potential applications of blockchain is far longer than this
John Accural
In financial services, chains of custody of a financial instrument is deeply regulated territory. This chain of custody is a very costly legacy process. The only way to speed this up is to securely & privately embed chains of identity/ownership into the very process. So, without proper Identity it will be possible for bad actors to continue to create the same chaos thats occurring today. You will need to be securely authenticated with the system and have the proper access controls to the information.
johnbuzz3
This can only occur if the transactions themselves are tied back to real world identities yet layered with security mechanisms that protect the privacy yet allow role based regulatory insight into the transactions themselves
AdaZombie
DLT securities market allows traders to buy or sell stocks directly on exchanges or directly to other market participants in a P2P manner without the intermediation services provided by a broker or clearinghouse
Tom299
Interesting read. As always
By including identity (either tokenized or privacy protection layer) we can allow regulatory controls over the movement of the value
Adam Spark Two
Check this one out: https://mck.co/2GZh8iP
Mac McFisher
Financial Institutions are faced with much higher regulatory, compliance costs as well as strict restrictions around capital exposure. These institutions are looking for innovative ways to reduce future regulatory and compliance costs as well as optimally manage their existing capital to generate new revenue streams.
Jack666
Many financial instruments are asset backed. The algorithmic version of “hard linking of the verified assets to the instruments/securities” and placing on a DLT will allow automation reconciliation of the accounts and instrument repricing. This will add a strong level of operational resiliency to capital markets utilizing asset linking to other instruments.
Adam Spikey
Additional use cases:
– A ledger that generally runs in a hostile environment like the public internet
– It uses cryptography to try and solve identity and ownership problems in this public environment
– It uses cryptography to try and automate business processes & reduce latency to accelerate the value of money
– Assets are on and managed on the ledger. Off ledger interactions are considered legacy, slow, and inefficient.
– Most real use cases of this technology are theoretical discussions, unimplemented, without a single live use case with enough scalability, security, or appropriate regulatory framework in place.
– Data on the DLT can be permissioned/private but all transactions on this ledger are public and all parties can see those transactions.
– DLT is the technology not the actual asset. The asset is the application utilizing the DLT (Stock trades, payments, swap trade, currencies, bonds & coupons, etc).
– Transactions are absolute, there is no reverting the transaction. Chargebacks/returns are a business process because the ledger cannot be reversed. You must initiate a transaction back to the originating party.
– Current DLT Identity & Data security mechanisms is ‘relatively unused’ cryptography built for financial services in 1990’s. These mathematics has a certain lifetime because computers and distributed calculations are getting faster & more efficient. The current cryptography is not resistive to quantum computer attacks, 5-10yr max additional lifetime, target window 2021-2026.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Thank you for sharing. Great selection. Exhaustive. I would potentially add cases on SCM – goods tracking & shipping
TomK
There is more
– Directly lending: Middle market direct lending: End consumer direct lending: Crowd source lending
– Insurance: Claims:
– Claims will require verifiable assets tied back to identity & proof of purchases
– Personal insurance. Chain of a lifetime. Buying a diamond you had a complete record of the crimes and claims against it?
– Codifying Contracts (ie Smart Contracts)
– Financial Services is expecting Smart Contracts to be a container for the execution of financial business transactions. These containers need stronger security and identity to assure all parties are known, trusted. Existing business models can be coded into Smart Contracts to accelerate the value of money.
ZoraBora
I thought the selling point of blockchain was an open, verifiable, immatuble history of transactions (or events) that anyone could check themselves.
You couldn’t get some shady repair shop to make up and backdate a service on a car and insert it into the car’s service-history-chain right before selling, for example.
Simon GEE
Another one would be posting of collateral for OTC trades. The posting of collateral & verified assets needs to be tied back to real world identities. Currently 3rd parties (ie clearing houses) are required as part of this step to validate real world ID and asset ownerships. Without DLT+Identity+VerifiableAssets it will be impossible to construct consensus algorithms to facilitate real-time settlement and measure trustworthiness.
johnbuzz3
Through the utilization of smart contracts, financial instruments can be pre-programmed to carry out corporate actions, such as payment of bond coupons or dividends
Adam Spikey
For the purpose of this article you should replace Blockchain with DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology). DLT is:
– A ledger that generally runs in a hostile environment like the public internet
– It uses cryptography to try and solve identity and ownership problems in this public environment
Zwierzak
Good examples. Inspiring. What about security?
Adam Spikey
… another great topic to discuss. What’s your point ?
Adam Spikey
… great topic for another post. What’s your point?
John McLean
Good article
TonyHor
When most people think of blockchain today, they think of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoins and Ethereum and Litecoin. That’s hardly surprising, as Bitcoin’s market ups and downs are breathlessly reported, sometimes on the front pages of newspapers. In fact, there are more than 800 cryptocurrencies traded on different stock markets… and they are just the tip of the blockchain iceberg. Lying beneath the water is the fact that technologies such as blockchain will allow small organizations, and even private individuals, making relatively small capital investments, to disrupt the global economic system by making p2p transactions more secure, reliable, and useful than the traditional trusted third-party. That’s a revolution, no more, no less.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Established banking industry is pouring money into blockchain technology far faster and more steadily, and a likely target of $$400 million during 2019.
Karel Doomm2
Thanks for sharing
JohnE3
It can not be concealed that blockchains and cryptocurrencies are new and conservatives tend to celebrate such inventions with a wide arc, but there are many wealthy people who are very interested in this technology, because even if it enables being anonymous. Even Bill Gates himself admitted to having BTC during one of the interviews. And the Winklevoss brothers and their investments in the crypto? For 10-20 years, cryptocurrencies may forget and maybe conquer the world like email or the internet.
Adam T
Intersting. What about crypto? and security issues?
Norbert Biedrzycki
See other articles. Example quantum comp
DDonovan
Blockchain has enormous potential also in many other segments, not only finances. Smart Contracts, which are based on the blockchain ethereum protocol, can help in the disgustingly complex system of settlements between the streaming platform and the artist. There are many blockchains – practically every cryptocurrency is a different blockchain. There are many applications for Fintech, banking, supply chain. This is definitely a huge future. And all in all it’s simple enough that a distributed and secure database.