Once people began to conduct transactions over distances greater than one man carrying a bag could travel, or that included more stuff than the bag could hold, a third-party (that people on both ends of the transaction trusted) became necessary. Why do we care about blockchain?
This is how we got money (with the trusted third-party the sovereign backing it), banks, and, ultimately, a financial system viewed as too big to fail… but which sometimes did.
Blockchain technology stores and transmits information on transactions conducted on the internet. A block contains information on a specific number of transactions. Depending on the network’s capacity, a new block of data is created every so often, and then another, and another, and so on, creating a kind of chain – a blockchain. The blocks are linked through complex mathematical algorithms.
A blockchain records and stores all the transactions concluded, along with information about them – the date, time, and parties to any transaction. Each node within a network (and there are tens of thousands of nodes) possesses a full copy of the blockchain in the form of a transaction ledger. Using complex mathematical and cryptographic rules, all transactions are verified by so-called miners, who also are responsible for creating new blocks. Additionally, the nodes within a network verify in an automatic and continuous manner both the transactions concluded and the entries in the transaction ledger. An attempt to cheat by modifying a concluded transaction, or entering an unauthorized one, will be foiled because the modification or fabrication won’t match the transaction records in the network ledger. So, it will be rejected.
All transactions recorded on the blockchain are public, while thousands of nodes simultaneously validate that a given transaction took place on day X at time Y. The blockchain itself – inhuman, disinterested, unable to forget – is the trusted third-party, affording all parties access to a single source of reliable and verified information.
Sounds good, doesn’t it?
That’s why we care about blockchain.
Transaction is information
Right now, blockchain technology can be applied to support many transactions (trade, currency, shares, stocks, and even electric energy). And work is now underway to use the blockchain as a ledger for banking, document certification systems, and digital signatures in public administration and notarial records. Theoretically, all these transactions could be concluded outside the system that has been in operation for many centuries, i.e., without institutions, and directly between the parties to a given transaction.
Of course, when most people think of blockchain today, they think of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoins and Ethereum and Litecoin. That’s hardly surprising, as Bitcoin’s market ups and downs are breathlessly reported, sometimes on the front pages of newspapers. In fact, there are more than 800 cryptocurrencies traded on different stock markets… and they are just the tip of the blockchain iceberg. Lying beneath the water is the fact that technologies such as blockchain will allow small organizations, and even private individuals, making relatively small capital investments, to disrupt the global economic system by making p2p transactions more secure, reliable, and useful than the traditional trusted third-party.
That’s a revolution, no more, no less.
The future is… maybe not yet
This is not to say the blockchain is the key to creating a decentralized financial system that will cover all humanity independent of governments, financial institutions, banks, intermediaries, and stock markets – a system too big to fail that won’t. But the current level of advancement of the blockchain, as well as the cryptocurrencies and innovations based on it, lead us to believe that we are on the path to creating just such a system.
The nature of blockchain technology (which is open source) will enable us to modify it as needed. (Perhaps some of its control and reconciliation elements will prove to be redundant.) Trade processes and information exchanges may become more transparent, faster, and considerably cheaper. It may no longer be necessary for governments and businesses to bear the costs of supporting a complicated global financial system, nor may people need to put their trust in anything other than the blockchain’s ones and zeroes – which are pretty trustworthy.
Public trust institutions such as banks, stock markets, and intermediaries in financial transactions see the enormous potential of blockchain technology, as well as its disruptive energy. They will need to transform themselves, or find themselves facing competition from organizations outside the ever-changing and evolving FinTech industry.
And that will be novel and, even better, unpredictable.
Related articles:
– Only God can count that fast – the world of quantum computing
– Blockchain – the ultimate financial crash
– Blockchain – the Holy Grail of the financial system?
– What is blockchain? All you need to know
– What are the bitcoins? All you need to know
– Blockchain has a potential to upend the key pillars of our society








Norbert Biedrzycki
Real blockchain use cases @101Blockchains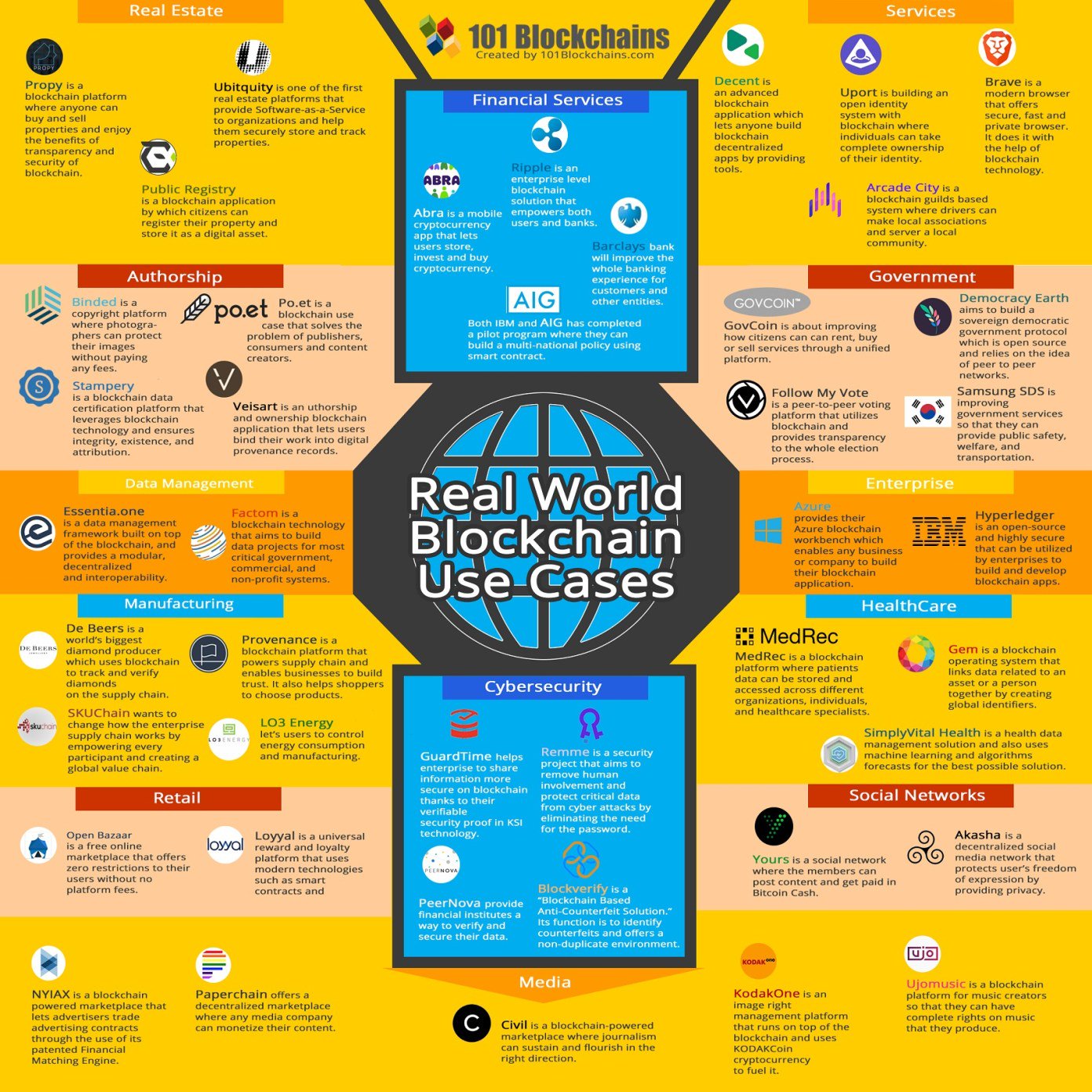
Tom Jonezz
Blockchain movement is causing a disruption on a massive scale by not only completely realigning the current global ecosystems but changing the way we live our lives. Cryptocurrencies are just one facet of the many promising use cases of the blockchain, which are being implemented globally to embrace this transparent, efficient & secure system.
Jack23
Blockchain != Bitcoin
Bitcoin == Blockchain
You can do a lot more with the Blockchain technology of immutable records (which it essentially boils down to). Unfortunately, due to poor programming there have been lost a great number of records (in this case cryptocurrency) in the past, because those records were no longer valid.
It is not safe, because it is not regulated (no oversight) and bad programming can/will result in you being broke in 10, if you use cryptocurrency.
Of course there can be errors. Mainly for ther reasons above (no oversight) and entire “chains” can be “lost in space” because their backtracking was diluted and/or not properly kept.
Blockchain != Bitcoin. Bitcoin aka Cryptocurrecy is the first use of the Blockchain technology (of immutable records). This was mainly (my personal view) to get rich quick on the inventor’s side.. The Blockchain technology is a great way to keep records i.e. for who owns which real estate and to whom was it sold, but it is far from “complete” or “error free”.
Use with caution. You have been warned!
CaffD
Depends on where you’re starting from… we taught from “Computational Complexity” by Papadimitriou and “Introduction to the Theory of Computation” by Sipser. The latter is probably fine if you don’t have a ton of CS knowledge from the get-go. Computational Complexity: A Conceptual Perspective has free drafts online, that’s another good book.
Here is a good overview of the most interesting aspects, including quantum stuff.
Nothing beats a course in it though. See if a university near you will let you audit a class, most profs don’t care
Norbert Biedrzycki
In reality, the relationship between the set of problems that can be solved in polynomial time with a quantum computer and other complexity classes that are solveable by classical computers isn’t fully known. It’s sort of related to the P =? NP problem, in that we might have some boundaries on what the complexity class encompasses, but without very rigorous, mathematical proofs that every problem in some complexity class is related to every problem in some other complexity class, you can’t fully relate the two classes. This isn’t to say that you literally have to show the relationship between every problem in one class to every problem in another (there are infinitely many trivially different problems in any class), but you have to distill away all of the trivial differences between problems in the same class to be able to say for sure that all problems in a class have these properties.
Oscar2
Building and scaling quantum networks is a formidable endeavor, requiring sustained and concerted efforts in physics, computer science, and engineering to succeed.
johnbuzz3
They utilized quantum machine learning, a special sub-field of machine learning that uses vector-like amplitudes rather than mere probabilities. The method of quantum machine learning being used is specially designed for low-qubit quantum computers, offloading some of the calculations to conventional processors.
AdaZombie
And the final stage will come when these quantum computers finally surpass their conventional cousins, making it possible to create distributed networks of computers capable of carrying out calculations that were previously impossible, and instantly and securely share them around the world.
Oscar2
What makes me wonder is stating that blockchain is better than the traditional databases; it is not, it is different. It has the entirely different purpose of existence. Secondly, in the first sentence, the article is noting that Bitcoin is just one iteration of blockchain (cryptocurrency network), while the author is referring to the Proof-of-Work type consensus which is strictly linked to the two largest cryptocurrencies: Ethereum and Bitcoin.
johnbuzz3
Through the utilization of smart contracts, financial instruments can be pre-programmed to carry out corporate actions, such as payment of bond coupons or dividends
Jack666
Many financial instruments are asset backed. The algorithmic version of “hard linking of the verified assets to the instruments/securities” and placing on a DLT will allow automation reconciliation of the accounts and instrument repricing. This will add a strong level of operational resiliency to capital markets utilizing asset linking to other instruments.
John Accural
In financial services, chains of custody of a financial instrument is deeply regulated territory. This chain of custody is a very costly legacy process. The only way to speed this up is to securely & privately embed chains of identity/ownership into the very process. So, without proper Identity it will be possible for bad actors to continue to create the same chaos thats occurring today. You will need to be securely authenticated with the system and have the proper access controls to the information.
AndrewJo
Identity and security layering will be required that trust (ie access to manipulate underlying assets), is granted only to bits of contacts/ledgers that need to interoperate
John McLean
The nation should seriously think about how it treats cryptocurrencies, not only from a regulation point of view, but also a tax treatment point of view
JohnE3
It can not be concealed that blockchains and cryptocurrencies are new and conservatives tend to celebrate such inventions with a wide arc, but there are many wealthy people who are very interested in this technology, because even if it enables being anonymous. Even Bill Gates himself admitted to having BTC during one of the interviews. And the Winklevoss brothers and their investments in the crypto? For 10-20 years, cryptocurrencies may forget and maybe conquer the world like email or the internet.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Established banking industry is pouring money into blockchain technology far faster and more steadily, and a likely target of $$400 million during 2019.
johnbuzz3
IMHO without proper Identity it will be possible for bad actors to continue to create the same chaos thats occurring today. You will need to be securely authenticated with the system and have the proper access controls to the information. As a result of this problem the majority of the capital market industry is focused on development of private/permissioned DLT that will never allow an Internet based browser access to these private networks. Access will likely occur via proprietary applications or proprietarty+embedded Webkit technology. By linking credentials to individuals, individuals and assets to corporate entities we can create unique cryptographic identification tagging to tradable instruments. Wrapped within a permissioned based privacy friendly security layer it will allow association of people and assets within a hostile environment (such as a public Blockchain running on the internet).
Oscar2
Blockchain is immutable. Reality: Blockchain uses immutable data structures. You might want to clarify how those 2 opposing statements (back to back) are both true.
Karel Doomm2
Gonna put voting on the blockchain? Great. How much energy are you going to waste to secure this block chain? Cause corporations or wealthy individuals would never use their wealth to affect the outcome of an election. Last presidential elections spent something like $7 billion. If someone could just get a bunch of servers and do a 51% attack for like $500 million dollars, it would be a good investment. Also, keep in mind, other nation states never interfere with elections….
So you need to probably burn a billion dollars worth of energy just to secure the election. Something like that. Maybe more if China wants to pick the next U.S. president.
TomCat
It’s ~50%, and after one use, it’s 128 bit security, which is equivalent to Bitcoin’s security. It’s statistically possible for it to be higher or lower. https://iota.stackexchange.com/questions/245/what-information-is-leaked-if-i-reuse-an-address
I guess you are insinuating that this is a bad tradeoff for quantum security? If so, I’d like to point out that wallets can be automated to deal with the issue and permanent address solutions are being created, so it’s a temporary inconvenience for a long term security measure. My guess is other coins will have to find solutions once quantum computers come online, and unless they have a plan in place and tested, they won’t have much time in which to work–as we are seeing with BLT it may have effects on other parts of coin design, so kicking the can down the road in hopes that quantum computers are a distant problem may not be the wiser option.
AdaZombie
The main advantages of a quantum communication network over a conventional one are speed and security. Entanglement makes it possible to communicate instantly across arbitrarily large distances in principle. No matter how far apart you put two entangled qubits, acting on one will have an instant and measurable impact on the other.
Jack666
There is a more important underlying question here that I don’t think a lot of people have thought about. If someone does break elliptic curve digital signature algorithm they will be able to steal a significant amount of coins from users on the bitcoin network. This would be obvious grounds for a hard fork — these funds were stolen because of a flaw in the bitcoin protocol
Karel Doomm2
What does “peer-to-peer, decentralized, append-only database” mean?
You probably know what a “database” is. Some people say it is sort of like an Excel spreadsheet. In the case of Bitcoin, the spreadsheet contains information about Bitcoin Wallets, which are like bank accounts.
“Append-only” means it is a database that you can add information to it, but you can never change the information that was added to it, and you can never take information away. This is important because you don’t want people cheating by changing information in the past to make it look like you have more Bitcoin money than you actually bought.
“Decentralized” means copies of the database exists on many, many different computers, and all of these computers can append information to the database. When new information is appended, the new information is copied to all of the computers.
“Peer-to-peer” means the database is not owned by any one company or person. Anyone can create a copy of the database and use the network. Everyone who has a copy of the database and connects to the network is an owner of the database.
Basically, blockchains are a technology, and like all other technologies, it can be used to solve various problems. Bitcoin is just one place where a blockchain is used.
Also, in my opinion, Bitcoin and crypto-currency is a waste of time and electricity, and I don’t think it will be very valuable for very long, it will probably suffer an economic crash in the near future. However the blockchain technology for Bitcoin is very interesting.
TomCat
it is possible to update to 512 or 1024 ecc, and the task will remain difficult. If think in ecc256 some mathematical vulnerability might be found as for RSA and this will need to apply new algorithm
Norbert Biedrzycki
If someone does break ECDSA they will be able to steal a significant amount of coins. Potential hard fork occurs — these funds were stolen because of a flaw in the bitcoin protocol
DDonovan
Blockchain has enormous potential also in many other segments, not only finances. Smart Contracts, which are based on the blockchain ethereum protocol, can help in the disgustingly complex system of settlements between the streaming platform and the artist. There are many blockchains – practically every cryptocurrency is a different blockchain. There are many applications for Fintech, banking, supply chain. This is definitely a huge future. And all in all it’s simple enough that a distributed and secure database.
Simon GEE
Another example: Posting of collateral for OTC trades. The posting of collateral & verified assets needs to be tied back to real world identities. Currently 3rd parties (ie clearing houses) are required as part of this step to validate real world ID and asset ownerships. Without DLT+Identity+VerifiableAssets it will be impossible to construct consensus algorithms to facilitate real-time settlement and measure trustworthiness.
TomK
Financial Services is expecting Smart Contracts to be a container for the execution of financial business transactions. These containers need stronger security and identity to assure all parties are known, trusted. Existing business models can be coded into Smart Contracts to accelerate the value of money.
TonyHor
… cannot be tampered with unless 50% of the machines working on that blockchain are run by the same group.
So, unless you have one of the world’s biggest block chains, it’s easy for someone to rent enough computers to have 51% temporarily, rewrite the block chain any way they want, and profit.
johnbuzz3
Some people claim that AI is threatening humanity. We think that blockchain can stop that, because AI is actually not that intelligent at the moment, so the threat is relatively low. But in a decade, two decades, AI will be really strong, a lot stronger than it is now. When AI is running on blockchain, on smart contracts, we can refrain AI. For example, we can write a blockchain algorithm to restrain the computational power of AI and keep it from acting on its own.
Simon GEE
By combining Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain technology, Decentralized peer-to-peer distributed technology and Quantum Computing technology, the “Computer System” will be able to understand the human emotions, so that it can handle the things or works which can only be handled by human. And then mankind can give the power to this “Computer System,” which has no humanity or human desire. It will be fair and equitable, and can not be cheated or tampered.
johnbuzz3
Many of blockchain startups in the space will either begin generating revenue – via providing products the market demands/values – or vaporize due to running out of cash. In other words, 2017 should be the year where there is more implementation of products utilizing blockchain tech, and less talk about blockchain tech being the magical pixie dust that can just be sprinkled atop everything.
DDonovan
For most high-yield usages (like banking backends), you simply don’t have to do that.
For a public blockchain, yepp.
Did Bitcoin stop being essentially owned by chinese miners, who could be forced by their government to change the blockchain at any moment?
TomCat
As web infrastructure, you don’t need to know about the blockchain for it to be useful in your life. Currently, finance offers the strongest use cases for the technology. International remittances, for instance. The World Bank estimates that over $430 billion US in money transfers were sent in 2015. And at the moment there is a high demand for blockchain developers.
TomHarber
and in 2016 it was more than 540
Norbert Biedrzycki
Classifications of Notable Cryptos
DDonovan
Blockchain is as an instrument that came to resolve the problem of monopoly. It can help to hold the honest voting in countries. It’s not the people who vote that count, it’s the people who count the votes. Thanks to blockchain technology it is not possible to erase the vote or change it. What’s more, it can influence the healthcare industry and resolve the energy issues.
AdaZombie
DLT securities market allows traders to buy or sell stocks directly on exchanges or directly to other market participants in a P2P manner without the intermediation services provided by a broker or clearinghouse
John McLean
The most critical area where Blockchain helps is to guarantee the validity of a transaction by recording it not only on a main register but a connected distributed system of registers, all of which are connected through a secure validation mechanism.
TomK
As revolutionary as it sounds, Blockchain truly is a mechanism to bring everyone to the highest degree of accountability. No more missed transactions, human or machine errors, or even an exchange that was not done with the consent of the parties involved.
Tom Jonezz
Banks are not gonna like it
Adam Spark Two
As the Internet commoditized the cost for communication, Ethereum commoditizes our costs of agreement and trust.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Sure, but only if ETH would be used more wildly not as a store of value but for a smart contracts as well
Adam Spark Two
The Blockchain protocol is the world’s largest modern-day abacus; it only enables us to move a bead (or coin) from one side to the other. The ability to do this on a global, permissionless substrate is not trivial. But I can’t overemphasize the limited scope of this initial design, due to its use of a virtual machine which isn’t Turing-complete.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Blockchain application goes beyond crypto only. Could be used in energy production and contract reconciliation, banking/insurance & finch, public sector as a trust document storage or value sharing … and many more
John Accural
How can blockchain help? First, it boosts affordability by reducing costs and waste, enabling the whole value chain to transact and share information in a trusted, easily auditable way. Second, it improves accountability and reduces fraud by offering greater real-time transparency across an organization’s entire value chain. These benefits then multiply and increase public trust in the organization’s capabilities, giving it a more compelling story to tell potential donors and to attract sustainable funding sources.
Norbert Biedrzycki
Very true. I would also add trusted data across whole of the value chain for all users, no limitations
TomK
Bitcoin was invented in 2008. Since that time, the Bitcoin blockchain has operated without significant disruption. To date, any of problems associated with Bitcoin have been due to hacking or mismanagement. In other words, these problems come from bad intention and human error, not flaws in the underlying concepts.
johnbuzz3
2017 was a great year for blockchain enthusiasts
TomHarber
… why? Do you see more stable applications of this technology except crypto?
John McLean
A global network of computers uses blockchain technology to jointly manage the database that records Bitcoin transactions. That is, Bitcoin is managed by its network, and not any one central authority. Decentralization means the network operates on a user-to-user (or peer-to-peer) basis. The forms of mass collaboration this makes possible are just beginning to be investigated.
Jack666
Perhaps that is my take-away: 2017 was the year that individual lawyers and law firms got over themselves and worked together, at least in the blockchain space.
My prediction: In 2018, the speed and scale of technological developments will make non-traditional legal teaming not just nice to have, but critical.
Mac McFisher
As a new generation of crypto users begin to invest in the technology, developers are growing concerned about its infrastructure. They’ve seen this happen before – new users enter the space attracted by big gains, then suddenly, a catastrophic failure, usually at the very exchanges designed to hold and custody those funds.
Simon GEE
2018 will be the year where the tremendous innovation and promise of blockchain must become real. Otherwise, the market is in for a rude awakening. And maybe that’s not the worst thing in the world.
Tom Jonezz
Right. Hope we are going to see more business applications than another 1000 cryptos
TomK
The biggest impact on the development of quantum computers will come from the financial sector, the industry and government institutions, who have a great interest in their development. In future articles, I will try to analyze the risks and benefits of quantum computers to some of these sectors.
Adam Spikey
God article. Check this one: 18 blockchain-related prediction for 2018 by a co-founder of ConsenSys Capital, the financial services offering constellation at ConsenSys including ConsenSys Ventures, Token Foundry, and ConsenSys Capital Asset Management at consensys.net
Norbert Biedrzycki
Very good read. Thanks for sharing
TomHarber
could you embed a link?
TomHarber
Here it is https://media.consensys.net/18-predictions-for-2018-7a376ea7bd4b